Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR)
TEVAR has emerged as an alternative to conventional open surgery.
Many of the patients who suffer from aortic conditions are elderly, frail and have a number of medical conditions – including patients who previously would not have qualified for any intervention. TEVAR thus increases the population of patients who can be treated.
The TEVAR procedure
Patients are typically put to sleep, and the TEVAR procedure is performed in a special operating theatre under X-ray guidance.
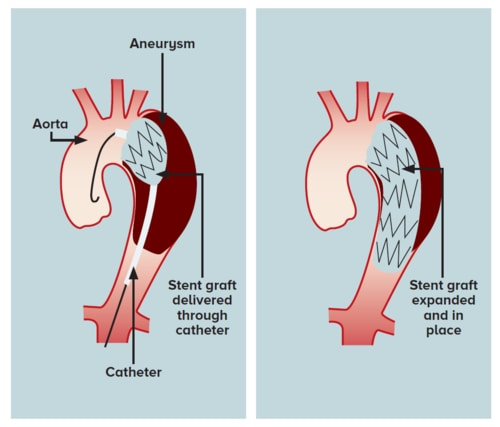
During the procedure, a tube or catheter is inserted into the blood vessel in the groin. A wire is guided through the artery into the major blood vessel of the body (aorta). A stent is delivered in a collapsed state and positioned accurately using X-ray guidance.
The stent is then expanded to span and cover the site of blood vessel injury. As a result, the stent lines and reinforces the torn blood vessel wall to ensure continuity of blood flow and prevent further bleeding.
This procedure usually takes about one to three hours.
Patients typically stay in the hospital for three to four days and can resume all regular activities within a month. Complex cases may require a longer procedure time and hospital stay. Follow-up is lifelong with serial scans.
TEVAR vs open surgery
The main risks of TEVAR include catastrophic paralysis which can be mitigated with various techniques. Other risks include bleeding, infection and stroke.
Overall, despite these risks, it also gives hope to patients who are at high or prohibitive surgical risk.
Enhancements
In the past, the blood vessel in the groin was accessed using a big cut and subsequently repaired. However, in recent times, keyhole devices have had success in furthering the procedure.
Today, the painful cut in the groin has been replaced by these revolutionary devices. The TEVAR procedure is evolving into a truly minimally invasive surgery.
In the last few years, TEVAR technology has had further enhancements. Stents can be custom-built for each patient’s blood vessel structure. However, the time needed to build each customized stent is about four to six weeks.
