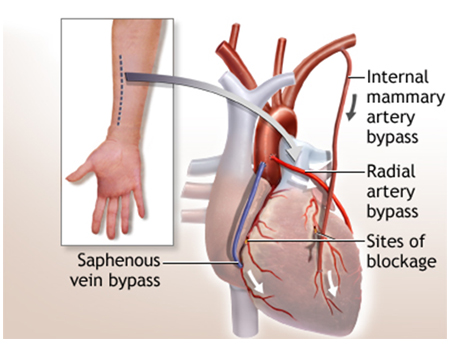
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), also called heart bypass surgery, is performed to improve blood flow to the heart. When indicated, it is the option that is proven to improve survival benefit, meaning people live longer.
It is recommended when coronary arteries are severely diseased or difficult to manage via stenting.
CABG involve using healthy blood vessels from another part of the body (chest, forearm, and legs) and connects them to blood vessels after the blocked artery. This creates a new pathway for blood to flow past the blockage. First foremost, it involves making an incision over the breastbone (sternum) to gain exposure to the heart. It is the difficulty of suturing or “sewing” two small blood vessels together, each about 1.5-2.0 mm diameter and making flow well.
On pump vs off pump CABG
In on pump CABG, your heart is stopped chemically, and a heart-lung machine takes over the function of the heart and lungs in supply blood throughout the body. This is the most common approach.
At times, this is not an option for some patients. Then off pump CABG is performed. In off pump CABG, the heart is not stopped. The same procedure is performed. It is technically more challenging. The difficulty of suturing or “sewing” on a moving target. It helped with the use of a stabilization equipment to keep the heart still. This equipment helps avoid use of the heart-lung machine by creating the same situation for the surgeon to accurately perform on the patient’s heart while it continues to beat.
Surgery has its risks and benefits. Benefits of improving symptoms and longevity are what makes CABG superior.