Hydration
Water, the elixir of life, is fundamental to our existence. It is the very essence of our being, the cornerstone of our health. In this article, we delve into the significance of hydration, exploring its impact on our body, mind, and overall well-being.
The Science of Hydration
At a cellular level, our bodies are predominantly made up of water, around 60%. This aqueous composition underscores the pivotal role water plays in our daily lives. It’s the solvent for chemical reactions, regulates body temperature, and acts as a transport system, carrying essential nutrients and oxygen to cells while removing waste products.
Understanding Dehydration
Dehydration is your body’s way of sounding the alarm that it’s running low on essential fluids. Common signs of dehydration include excessive thirst, dry mouth, dark urine, fatigue, and dizziness. In severe cases, it can lead to confusion, rapid heartbeat, and fainting. Your body craves water to function optimally, and neglecting its need can have dire consequences.
Daily Hydration Requirements
The golden rule for daily water intake is often quoted as eight 8-ounce glasses, totaling about 2 liters (or half a gallon). However, individual needs vary. Factors like climate, physical activity, and overall health play a significant role. A more accurate approach is to listen to your body; it has a way of letting you know when it’s time for a water break.
Hydration and Physical Performance
For those engaged in physical activities or sports, proper hydration is paramount. Dehydration can lead to a significant decrease in physical performance. Even a loss of 2% of your body’s water content can result in reduced endurance and strength, making staying hydrated during exercise crucial.
Hydration and Cognitive Function
Dehydration doesn’t only affect your physical state; it also impairs cognitive function. Your brain, like any other organ, needs sufficient hydration to perform optimally. Dehydration can lead to problems with short-term memory, concentration, and alertness.
Hydration and Weight Management
Water has the remarkable ability to aid in weight management. Drinking a glass of water before a meal can help control appetite, prevent overeating, and promote a feeling of fullness. Additionally, water assists in breaking down food and promoting healthy digestion.

Hydration Tips:
Make it a habit : Incorporate regular sips of water into your daily routine.
Variety is key : While water is the primary source of hydration, juicy fruits and vegetables also contribute. Cucumbers, watermelons, and oranges are excellent sources of hydration.
Herbal teas : If plain water feels monotonous, herbal teas or infused water can be a flavorful, hydrating alternative.
Know your body : Pay attention to the signals your body sends. Thirst is your body’s way of asking for water.
Rehydration after exercise : After a workout, rehydrate with water and, if needed, an electrolyte drink to restore essential minerals lost through sweat.
Conclusion
Hydration is not merely a choice; it’s a lifestyle. Embrace the profound impact that proper hydration can have on your body and mind. From enhancing physical performance to sharpening cognitive abilities and promoting overall health, the benefits are vast. Drink up, for water is your silent ally on your journey to a vibrant, well-hydrated life.
Fish Diet: Benefits, Drawbacks, and Healthy Ways to Incorporate Fish Into Your Diet
Fish is a nutritious and delicious food that can be incorporated into a healthy diet in a variety of ways. It is a good source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and other essential nutrients.
Benefits of a Fish Diet
There are several potential benefits to following a fish diet, including:
Improved heart health: Fish is a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart health. Omega-3 fatty acids can help to lower cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and improve blood vessel function.
Reduced risk of stroke: Fish consumption has been linked to a reduced risk of stroke. This is likely due to the omega-3 fatty acids in fish, which can help to prevent blood clots from forming.
Improved brain health: Omega-3 fatty acids are also important for brain health. They can help to improve cognitive function, memory, and mood.
Reduced risk of cancer: Some studies have shown that eating fish may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as colon cancer and breast cancer.
Weight loss and maintenance: Fish is a low-calorie, high-protein food. This means that it can help you feel full and satisfied after eating, while also helping you to create a calorie deficit, which is necessary for weight loss.
Improved bone health: Fish is a good source of vitamin D, which is important for bone health. Vitamin D helps to absorb calcium, which is essential for maintaining strong bones.
Drawbacks of a Fish Diet
While there are several potential benefits to following a fish diet, there are also some drawbacks to be aware of:
Mercury contamination: Some types of fish, such as swordfish and king mackerel, can contain high levels of mercury. Mercury is a neurotoxin that can damage the nervous system, especially in children and developing fetuses. It is important to choose fish that are low in mercury, such as salmon, tuna, and shrimp.
- Overfishing: Some types of fish, such as cod and halibut, are overfished. This means that they are caught at a faster rate than they can reproduce. Overfishing can lead to the collapse of fish populations and damage to the marine environment. It is important to choose fish that are sustainably harvested.
Healthy Ways to Incorporate Fish Into Your Diet
There are many healthy ways to incorporate fish into your diet. Here are a few tips:
Eat at least two servings of fish per week: The American Heart Association recommends eating at least two servings of fish per week, especially fatty fish.
Choose a variety of fish: There are many different types of fish to choose from, so try to eat a variety. This will help you to get the most nutrients from fish.
Cook fish in healthy ways: Grill, bake, or steam fish instead of frying it. This will help to reduce the amount of fat and calories in your meals.
Serve fish with healthy sides: Pair fish with healthy sides, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This will help to create a balanced and nutritious meal.
Here are some examples of healthy fish-based meals:
Salmon grilled with roasted vegetables
Tuna salad sandwich on whole-wheat bread
Fish tacos with whole-wheat tortillas and vegetables
Fish stew with vegetables and quinoa
Shrimp stir-fry with brown rice and vegetables
By following these tips, you can incorporate fish into your diet in a healthy and sustainable way.

Mushrooms in Diet: A Nutritious and Delicious Addition
Mushrooms are a delicious and nutritious food that can be incorporated into a healthy diet in a variety of ways. They are a good source of protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and they have been linked to a number of health benefits.
One of the most well-known health benefits of mushrooms is their ability to boost the immune system. Mushrooms contain compounds called beta-glucans, which have been shown to activate white blood cells and help the body fight off infection.
Mushrooms are also a good source of antioxidants. Antioxidants help to protect the body from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
In addition to their immune-boosting and antioxidant properties, mushrooms have also been shown to have a number of other health benefits, including:
- Reducing the risk of heart disease
- Lowering cholesterol levels
- Regulating blood sugar levels
- Promoting gut health
- Supporting brain health
Mushrooms are also a low-calorie food, making them a good choice for people who are trying to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight.
How to Incorporate Mushrooms into Your Diet
There are many ways to incorporate mushrooms into your diet. Here are a few ideas:
- Add mushrooms to soups, stews, and stir-fries.
- Sauté mushrooms with garlic and olive oil for a simple and delicious side dish.
- Grill or bake mushrooms with your favorite herbs and spices.
- Stuff mushrooms with cheese, bread crumbs, and other ingredients for a tasty appetizer or main course.
- Add mushrooms to smoothies and juices for a boost of nutrition.
Tips for Choosing and Preparing Mushrooms
Conclusion:
Mushrooms are a nutritious and delicious food that can be incorporated into a healthy diet in a variety of ways. They are a good source of protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and they have been linked to a number of health benefits.
So next time you’re looking for a healthy and delicious meal or snack, reach for some mushrooms!
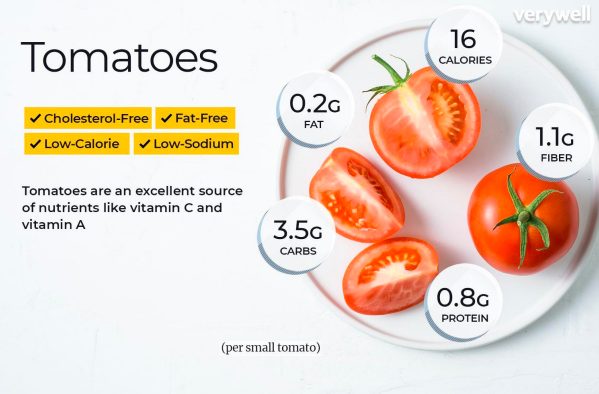
Tomatoes: A Tasty and Nutritious Fruit for a HealthyDiet
Tomatoes are a popular fruit that is often enjoyed in salads, sandwiches, and other
dishes. They are also a good source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Nutritional Value of Tomatoes
One cup of chopped tomatoes contains the following:
- Calories: 32
- Protein: 1 gram
- Fat: 0 grams
- Fiber: 2 grams
- Vitamin C: 24% of the daily recommended value (DV)
- Vitamin A: 12% of the DV
- Vitamin K: 10% of the DV
- Potassium: 9% of the DV
- Folate: 6% of the DV
Tomatoes are also a good source of other vitamins and minerals, including vitamin
E, niacin, magnesium, and copper.
Health Benefits of Tomatoes
Tomatoes have been linked to a number of health benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of cancer: Tomatoes contain lycopene, a powerful antioxidant that has been shown to protect against certain types of cancer, such as prostate cancer, lung cancer, and stomach cancer.
- Improved heart health: Lycopene can also help to lower cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation, which can improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Stronger bones: Tomatoes are a good source of vitamin K, which is important for bone health. Vitamin K helps to produce osteocalcin, a protein that helps to keep calcium in the bones.
- Better eye health: Tomatoes contain lutein and zeaxanthin, two carotenoids that are important for eye health. Lutein and zeaxanthin can help to protect against age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of blindness in older adults.
How to Incorporate Tomatoes into Your Diet
Tomatoes are a versatile fruit that can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. They can be eaten fresh, cooked, or canned. Tomatoes can also be added to soups, stews, sauces, and other dishes.
Here are a few tips for incorporating tomatoes into your diet:
- Add chopped tomatoes to your favorite salad
- Slice tomatoes and top your sandwich or burger.
- Use canned tomatoes to make a simple tomato sauce for pasta or pizza.
- Add diced tomatoes to your favorite soup or stew.
- Make a gazpacho or tomato soup for a refreshing and nutritious meal or
snack.
Conclusion:
Tomatoes are a tasty and nutritious fruit that can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. They are a good source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, and they have been linked to a number of health benefits. So next time you’re looking for a healthy and delicious meal or snack, reach for some tomatoes!

Chicken Diet: Benefits, Drawbacks, and Healthy Waysto Incorporate Chicken Into Your Diet
Chicken is a popular meat choice for people of all ages and dietary needs. It is a good source of protein, low in saturated fat, and relatively affordable. As a result, many people choose to follow a chicken-based diet.
Benefits of a Chicken Diet
There are several potential benefits to following a chicken diet, including:
- Weight loss: Chicken is a low-calorie, high-protein food. This means that it can help you feel full and satisfied after eating, while also helping you to create a calorie deficit, which is necessary for weight loss.
- Muscle growth and repair: Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissue. Chicken is a good source of protein, making it a good choice for people who are trying to build or maintain muscle mass.
- Reduced risk of heart disease: Chicken is a low-saturated fat food. Saturated fat can raise cholesterol levels, which can increase your risk of heart disease. Eating chicken instead of other high-saturated fat meats may help to reduce your risk of heart disease.
- Improved bone health: Chicken is a good source of phosphorus, which is important for bone health. Phosphorus helps to maintain bone mineral density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Drawbacks of a Chicken Diet
While there are several potential benefits to following a chicken diet, there are also some drawbacks to be aware of:
- Nutrient deficiencies: If you rely too heavily on chicken as your sole source of protein, you may be at risk of developing nutrient deficiencies. Chicken is low in some nutrients, such as fiber, calcium, and iron. It is important to include other foods in your diet to ensure that you are getting all of the nutrients that you need.
- Unhealthy eating habits: It is possible to follow a chicken diet in an unhealthy way. For example, you may be tempted to eat fried chicken or processed chicken products, which are high in unhealthy fats and sodium. It is important to choose healthy cooking methods and to avoid processed chicken products when following a chicken diet.
- Unsustainability: A chicken-based diet can be difficult to follow in the long term. It can become repetitive and boring to eat chicken every day. Additionally, you may miss out on other healthy and delicious foods if you are only eating chicken.
Healthy Ways to Incorporate Chicken Into Your Diet
If you are interested in following a chicken diet, there are a few things you can do to make sure that it is healthy and sustainable:
- Choose lean cuts of chicken: When choosing chicken, opt for lean cuts, such as boneless, skinless chicken breast or thigh. These cuts are lower in saturated fat and calories than other cuts of chicken.
- Cook chicken in healthy ways: Grill, bake, or steam chicken instead of frying it. This will help to reduce the amount of fat and calories in your meals.
- Pair chicken with other healthy foods: Include a variety of other healthy foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This will help to ensure that you are getting all of the nutrients that you need.
Here are some examples of healthy chicken-based meals:
- Chicken breast grilled with roasted vegetables
- Chicken stir-fry with brown rice
- Chicken salad sandwich on whole-wheat bread
- Chicken soup with quinoa
- Chicken and vegetable chili
By following these tips, you can incorporate chicken into your diet in a healthy and sustainable way.


Brussels Sprouts: A Nutritious and Delicious Vegetable
Brussels sprouts are a member of the cruciferous vegetable family, which also includes broccoli, cauliflower, and kale. They are a good source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, and they have been linked to a number of health benefits.
Nutritional Value of Brussels Sprouts
Brussels sprouts are a low-calorie vegetable that is packed with nutrients. One cup of cooked Brussels sprouts contains the following:
- Calories: 56
- Protein: 3 grams
- Fiber: 4 grams
- Vitamin C: 100% of the daily recommended value (DV)
- Vitamin K: 137% of the DV
- Manganese: 25% of the DV
- Potassium: 10% of the DV
- Folate: 10% of the DV
Brussels sprouts are also a good source of other vitamins and minerals, including vitamin A, vitamin B6, and magnesium.
Health Benefits of Brussels Sprouts
Brussels sprouts have been linked to a number of health benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of cancer: Cruciferous vegetables, including Brussels sprouts, contain compounds that have been shown to have anti-cancer properties. Studies have shown that eating Brussels sprouts may be associated with a reduced risk of certain types of cancer, such as colon cancer, lung cancer, and breast cancer.
- Improved heart health: Brussels sprouts contain compounds that can help to lower cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation. These effects can help to improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Better gut health: Brussels sprouts are a good source of fiber, which is important for maintaining gut health. Fiber helps to promote regular bowel movements and feed the beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Stronger bones: Brussels sprouts are a good source of vitamin K, which is important for bone health. Vitamin K helps to produce osteocalcin, a protein that helps to keep calcium in the bones.
How to Incorporate Brussels Sprouts into Your Diet
Brussels sprouts can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. They can be roasted, steamed, grilled, or boiled. Brussels sprouts can also be added to soups, stews, and stir-fries.
Here are a few tips for incorporating Brussels sprouts into your diet:
- Roast Brussels sprouts with olive oil, salt, and pepper for a simple and delicious side dish.
- Add Brussels sprouts to your favorite soup or stew recipe.
- Stir-fry Brussels sprouts with garlic, ginger, and soy sauce for a quick and easy meal.
- Shred Brussels sprouts and add them to your favorite salad.
- Top your pizza with Brussels sprouts for a nutritious and flavorful twist.

Conclusion
Brussels sprouts are a nutritious and versatile vegetable that can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. They are a good source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, and they have been linked to a number of health benefits. So next time you’re looking for a healthy and delicious meal or snack, reach for some Brussels sprouts!
Unlocking the Power of a Healthy Diet: Elevating Your Well-Being and Vitality
In a world that bombards us with tantalizing quick meals and convenient food options, maintaining a healthy diet often takes a back seat in our daily lives. A healthy diet is the cornerstone of nourishing the body with the essential nutrients it craves, in just the right measure. In this article, we embark on a journey to explore the facets, essentials, and advantages of embracing a healthy diet for a vibrant and active lifestyle.
Components of a Healthy Diet
Fruits and Vegetables
A kaleidoscope of fruits and vegetables gifts the body with a diverse spectrum of nutrients: an array of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, among other essentials.
Lean Proteins
Integrate protein-rich foods such as poultry, fish, tofu, legumes (beans and lentils), and lean cuts of red meat into your diet for optimal nutrition.
Whole Grains
Opt for whole grains like whole wheat, brown rice, quinoa, and oats over their refined counterparts. These complex carbohydrates supercharge energy levels and bolster digestion.
Healthy Fats
The body’s cravings for healthy fats are met with sources like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, abundant in omega-3 fatty acids.
Limiting Processed Foods and Added Sugars
In tandem with enriching your diet with healthy elements, curbing processed foods and sugar intake is paramount. Their adverse impact on metabolism and overall bodily function escalates the risk of various diseases and health maladies.
Fundamentals of a Healthy Diet
Balanced Nutrition
A harmonious blend of nutrients is the cornerstone of a healthy diet, categorized into two pivotal types: Macronutrients and Micronutrients. This equilibrium fuels proper body growth and nurtures a wholesome life.
Adequate Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is a non-negotiable for efficient digestion, temperature regulation, circulation, and cellular activities. The magic number for a healthy individual is around 3000 ml of daily water intake.
Portion Control
It’s not just about what we eat but also how much we consume that shapes our health. Understanding portion control is a key piece of the puzzle, ensuring we avoid overindulgence and maintain an ideal weight.

Benefits of a Healthy Diet
Weight Management
A pivotal advantage of a healthy diet is effective weight management. When balanced nutrition meets portion control, it’s a recipe for achieving and sustaining your desired weight.
Improved Overall Health
Meeting the body’s nutritional needs results in enhanced overall health and a reduced risk of diseases or health complications.
Enhanced Energy Levels
A nutritious diet is your steadfast ally for maintaining vitality and attentiveness throughout the day, ultimately enhancing your performance in daily activities.
Conclusion
Every morsel you consume is a vital investment in your well-being. This investment yields remarkable dividends in the form of a healthier, happier life. The insights and guidance shared above can serve as your compass on the journey to a better self, where you’ll experience a transformative difference.Unlocking the Power of a Healthy Diet: Elevating Your Well-Being and Vitality
The Heart Workout ; Power of Exercise for a Healthy Heart
Have you ever wondered how important physical activity is in our lives? Do you know that over 5 million lives can be saved each year if all inactive individuals become active? All these mortalities are attributed to heart diseases which are caused by physical inactivity.
A healthy heart is the foundation of overall well-being. Regular exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health. In this comprehensive overview, we’ll explore the importance of exercise for heart health, its benefits, and various types of exercises that can help you achieve and maintain a strong and healthy heart. Moreover we’ll also have a discussion about physical inactivity and why it occurs.
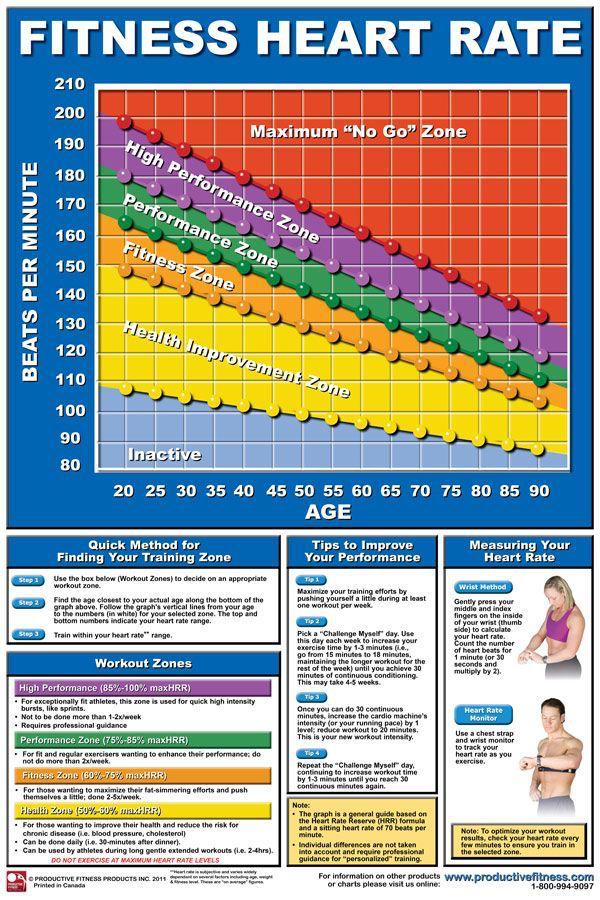
Importance of exercise for heart :
Exercise is of great importance for the health of your heart. According to research, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (and even light exercise as well) has been associated with lower incidence of cardiovascular diseases.
When you engage in exercising activities, your heart has to work harder to pump blood, which ultimately makes it more strong and efficient.
Physical Inactivity :
Worldwide, almost 30% of the people fail to meet the physical activity recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO).
It can be due to various factors which include sedentary lifestyles, time constraints, lack of access to exercise facilities, and varying levels of awareness regarding the importance of physical activity for health.
Additionally, the demands of modern life such as desk jobs or social media addictions can contribute to reduced physical activity levels.
Benefits of Exercise for heart :
Exercise has unlimited benefits on your heart, some of which include:
- Strengthens the Heart Muscle
- Improves Blood Circulation
- Manages Cholesterol Levels
- Enhances Cardiorespiratory Fitness
- Aids in Weight Management
- Enhances Insulin Sensitivity (which treats diabetes, a risk factor of heart diseases)
It’s important to note that the benefits of exercise for heart health are dose-dependent, meaning that the more you exercise, the greater the benefits.
Types of Exercises :
To promote heart health, it’s important to include a variety of exercise types in your fitness routine.
Here are some key types of exercises that benefit your heart:
1. Aerobic Exercises
These exercises increase your heart rate and breathing. They are great for improving overall cardiovascular fitness.
Examples:
- Brisk Walking: An excellent low-impact exercise for all fitness levels.
- Running or Jogging: Higher intensity, great for cardiovascular fitness.
- Cycling: A low-impact exercise that’s easy on the joints.
- Swimming: A full-body workout that’s gentle on joints.
- Dancing: A fun way to get your heart rate up.

2. Strength Training
Building muscle through resistance exercises can improve your metabolism and support overall heart health.
Examples:
- Weight Lifting
- Bodyweight Exercises (push-ups, squats, and planks)
- Resistance Bands
3. Flexibility and Stretching
Stretching exercises improve flexibility and can help reduce the risk of injury during other forms of exercise.
Examples:
- Yoga: A holistic practice that combines stretching, strength, and relaxation
- Static Stretching: Holding stretches for specific muscle groups
4. Sports and Recreational Activities
Engaging in sports or activities you enjoy is an excellent way to improve heart health.
Examples:
- Tennis
- Basketball
- Hiking
- Golf
To exercise safely, always warm up first and then progress gradually. Stay hydrated throughout, and after exercising, cool down to gradually lower your heart rate.