Heart Disease – Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
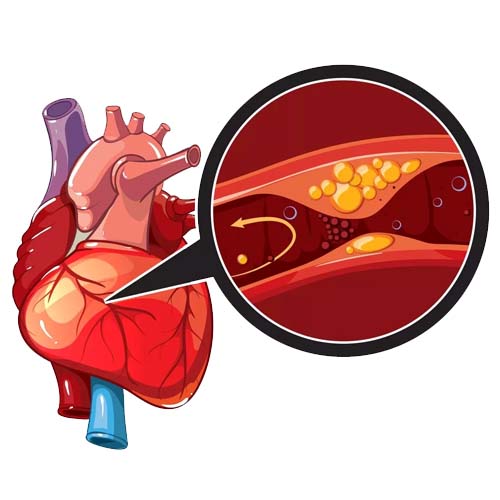
Coronary artery disease is commonly referred to as Heart Disease in Singapore. It is one of most common causes of death.
It describes problems involving your heart’s blood supply. It is interrupted by a build-up of fatty substances in the coronary arteries. Over time, the walls of your arteries can become furred up with fatty deposits. This process is known as atherosclerosis and the fatty deposits are called atheroma.
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), also called heart bypass surgery, is performed to improve blood flow to the heart. When indicated, it is the option that is proven to improve survival benefit, meaning people live longer.
CABG involve using healthy blood vessels from another part of the body (chest, forearm and legs) and connects them to blood vessels after the blocked artery. This creates a new pathway for blood to flow past the blockage. First foremost, it involves making an incision over the breastbone (sternum) to gain exposure to the heart. It is the difficulty of suturing or “sewing” two small blood vessels together, each about 1.5-2.0 mm diameter and making flow well.
Non-modifiable risk factors
- Age
- Gender
- Race
- Family History
- Menopause
Modifiable risk factors
- High blood cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes mellitus and abnormal high blood sugar levels
- Obesity and overweight
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
Treating coronary heart disease (CHD)
- Changing the modifiable risk factors
- Medicines – Thin the blood vessels and preventing stress of your heart
- Angioplasty – where balloons and stents are used to open narrow heart arteries
- Surgery – Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
Diagnosis – How can we find out?
- Treadmill test. One exerts and heart disease can show up on ECG or imaging.
- Radionuclide scan. Injecting a dye and stressing the heart can help differentiate the issues.
- CT scan. Less invasive to investigate coronary artery disease.
- Invasive coronary angiography. It is an invasive diagnostic procedure that involves taking X-rays of the heart’s arteries (coronary arteries).